Amblyomma americanum, or the lone star tick
Clinical considerations
The Amblyomma americanum tick is known for its ability to transmit the bacteria Ehrlichia chaffeensis, the agent responsible for human monocytic ehrlichiosis, Ehrlichia ewingii, the agent responsible for human granulocytic ehrlichiosis, and Francisella tularensis, the agent responsible for turalemia.
Geographical distribution
There is no evidence of established populations of lone star ticks in Québec. There is nevertheless a small risk of being bitten by this tick species given the presence of adventitious ticks.
Morphological characteristics
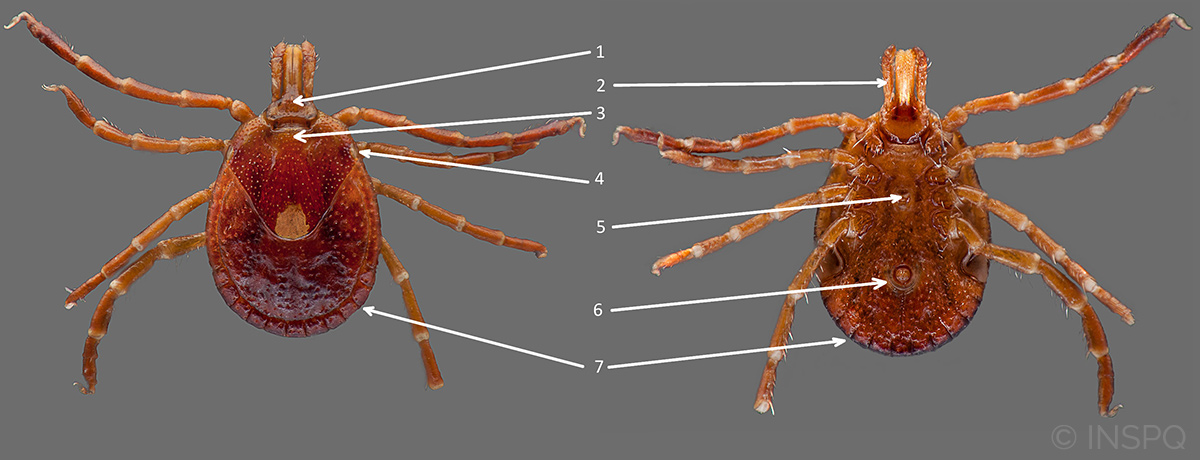
Amblyomma americanum in the female stage
Dorsal surface and ventral surface of the Amblyomma americanum tick in the female stage.
Head
1 - Basis capituli rectangular
2 - Long palps (palps are longer than the basis capituli)
Abdomen
3 - Partial shield, ornate with a whitish spot on its posterior end
4 - Presence of eyes
5 - Presence of genital pore
6 - Anal groove below the anus
7 - Presence of festoons (band of grooves and ridges on posterior margin of abdomen)
Did you know?
Ticks can travel on the backs of birds! While this rarely occurs, it is possible to get bitten by a tick that does not usually reside in Québec. For example, a tick may attach to a bird to take its blood meal and travel with the latter for several days. At the end of its meal, the tick detaches, moults and starts looking for a new host in its new environment, which can sometimes be located hundreds of kilometres from its place of origin. Such ticks are called adventitious ticks.
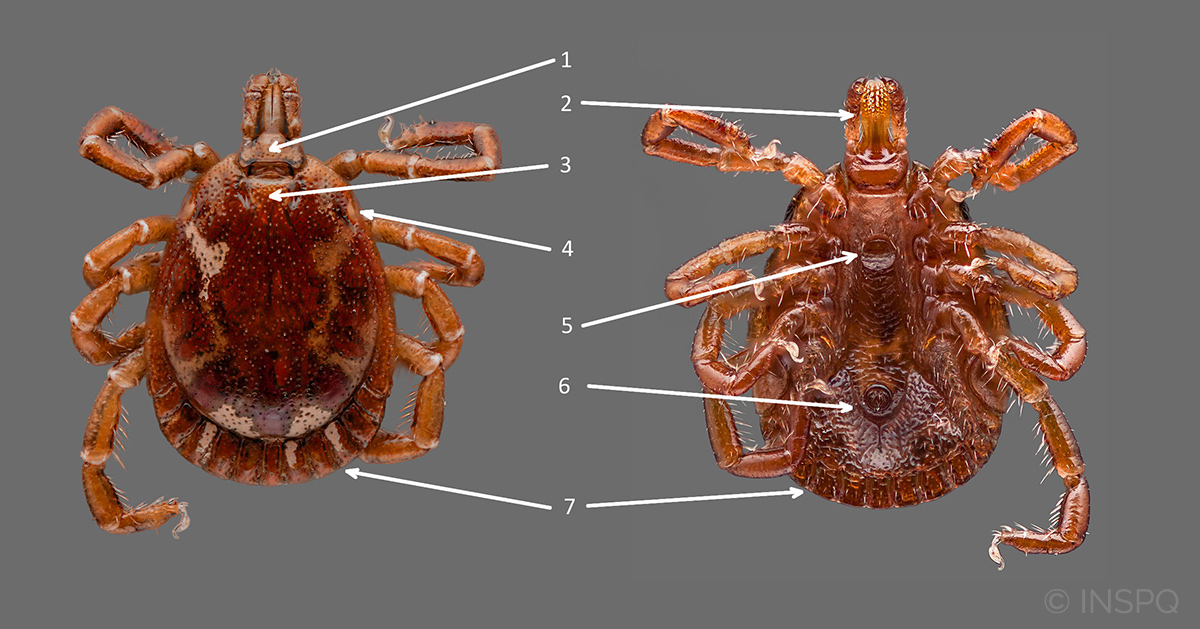
Amblyomma americanum in the male stage
Dorsal surface and ventral surface of the Amblyomma americanum tick in the male stage.
Head
1 - Basis of capituli rectangular
2 - Long palps (longer than the basis capituli)
Abdomen
3 - Complete shield, ornate with a few clear spots on the periphery
4 - Presence of eyes
5 - Presence of genital pore
6 - Anal groove below the anus
7 - Presence of festoons (band of grooves and ridges on posterior margin of abdomen)