Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci Infections Surveillance results: 2016-2017

From April 1st, 2016 to March 31st, 2017, 89 healthcare facilities took part in the surveillance of vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) infections, for a combined total of 4,827,659 patient days (Table 1). These facilities reported 44 healthcare-associated VRE (HA-VRE) infections, either acquired during a current or previous hospitalization (categories 1a and 1b). The HA-VRE infection rate was 0.09 per 10,000 patient days. This incidence rate was down from 2015-2016. The acquisition rate of HA-VRE colonization (cat. 1a and 1b) in 2016-2017 was 7.43 per 10,000 patient days and was lower compared to 2015-2016. For all results, analyses include facilities that participated for a minimum of 11 periods. Data were extracted on June 1st, 2017.
Update: October 5, 2017
Version française
Table 1 – Participation of Healthcare Facilities in the Surveillance of VRE Infections, Québec, 2012–2013 to
2016-2017
2012-2013 | 2013-2014** | 2014-2015 | 2015-2016 | 2016-2017 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Participating facilities (N) | 89 | 88 | 86 | 89 | 89 |
| Admissions (N) | 640,421 | 637,236 | 623,360 | 659,552 | 676,537 |
| Patient days (N) | 5,011,849 | 4,844,963 | 4,695,629 | 4,844,076 | 4,827,659 |
| Healthcare-associated VRE infections (cat. 1a and 1b) (N) | 41* | 88 | 89 | 82 | 44 |
| Healthcare-associated VRE colonizations (cat. 1a and 1b) (N) | 4,145 | 5,140 | 4,628 | 4,687 | 3,587 |
| Infected patients (cat. 1a and 1b) (N) |
| 86 | 85 | 79 | 42 |
* This datum excludes the 66 infections detected in patients already known to have VRE because the origin of their infection was not sought.
** Since 2013-2014, VRE infections include infections occurring among known VRE carriers.
Note: Colonizations include infections occurring among known carriers.
Incidence rates
In 2016–2017, the HA-VRE infection rate (cat. 1a and 1b) is 0.09 per 10,000 patient days for healthcare facilities participating in the last year (Table 2) as well as for those participating in the last five years (Table 3).
In the Montréal health region, teaching facilities have a tenfold higher HA-VRE infection rate than teaching facilities from outside the Montréal region (Table 2).
Table 2 – Incidence Rate and Percentile Distribution of Healthcare-Associated VRE Infection (Cat. 1a and 1b) by Type of Facility and Regional Categories, Québec, 2016–2017 (Incidence Rate per 10,000 Patient Days [95% CI])
| Healthcare facilities | Healthcare facility vocation | Min. | 25% | 50% | 75% | 90% | Max. | Incidence rate [95% CI] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Montréal health region | Non-teaching (N = 6) | 0 | 0 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.13 [0.05 ; 0.32] |
| Teaching (N = 14) | 0 | 0 | 0.05 | 0.20 | 0.53 | 0.56 | 0.22 [0.15 ; 0.32] | |
| Outside the Montréal health region | Non-teaching (N = 57) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.75 | 0.05 [0.03 ; 0.09] |
| Teaching (N = 12) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.08 | 0.16 | 0.02 [0.01 ; 0.07]* | |
| Total (N = 89) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.14 | 0.75 | 0.09 [0.07 ; 0.12] |
[95% CI]: 95% confidence interval.
* Significant statistical difference (p < 0.05) between the incidence rates of teaching healthcare facilities from the Montréal health region and outside the Montréal health region.
Incidence rate trends
In 2016-2017, the HA-VRE infection rate is statistically and significantly lower as compared to 2015-2016 (Table 3).This rate drop is mainly attributed to the decrease of the incidence rate in teaching healthcare facilities in the Montréal health region.
Table 3 – Incidence Rate of Healthcare-Associated VRE Infection (Cat. 1a and 1b) by Type of Facility and Regional Category, Québec, 2012–2013 to 2016–2017 (Incidence Rate per 10,000 Patient Days [95% CI])
| Healthcare facilities | Healthcare facility vocation | 2012-2013 | 2013-2014 | 2014-2015 | 2015-2016 | 2016-2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Montréal health region | Non-teaching (N = 5) | 0.12 [0.05 ; 0.31] | 0.18 [0.08 ; 0.39] | 0.17 [0.07 ; 0.39] | 0.23 [0.12 ; 0.46] | 0.14 [0.06 ; 0.34] |
| Teaching (N = 11) | 0.29 [0.20 ; 0.42] | 0.66 [0.52 ; 0.84] | 0.61 [0.47 ; 0.78] | 0.53 [0.40 ; 0.70] | 0.24 [0.16 ; 0.36]* | |
| Outside the Montréal health region | Non-teaching (N = 55) | 0.03 [0.01 ; 0.06] | 0.02 [0.01 ; 0.06] | 0.08 [0.05 ; 0.13] | 0.06 [0.03 ; 0.10] | 0.05 [0.03 ; 0.09] |
| Teaching (N = 12) | 0 | 0.03 [0.01 ; 0.08] | 0.03 [0.01 ; 0.08] | 0.02 [0.01 ; 0.07] | 0.02 [0.01 ; 0.07] | |
| Total (N = 83) | 0.09 [0.07 ; 0.12] | 0.18 [0.15 ; 0.22] | 0.19 [0.15 ; 0.23] | 0.16 [0.13 ; 0.20] | 0.09 [0.07 ; 0.12]* |
Note: Data are those from facilities that participated in the surveillance for a minimum of 11 periods every year between 2012-2013 and 2016-2017.
* Significant statistical difference (p < 0.05) between the incidence rates of 2015-2016 and 2016-2017.
Figure 1 – Incidence Rate of Healthcare-Associated VRE Infection (Cat. 1a and 1b) by Type of Facility and Regional Category (N = 83), Québec, 2012–2013 to 2016–2017 (Incidence Rate per 10,000 Patient Days [95% CI])
Note: Data are those from facilities that participated in the surveillance for a minimum of 11 periods every year between 2012-2013 and 2016-2017.
Description of cases
A total of 60 cases of VRE infection are reported: 47 (78.3%) are acquired in the participating healthcare facilities, either during hospitalization (N=43), a previous hospitalization (N=1) or in ambulatory care (N=3) (cat. 1a, 1b and 1c). Thirteen cases are linked to a stay in a non-reporting or community-based facility (category 2 and 3). No cases are of unknown origin (category 4) (Table 4). Of the 60 VRE infections, 38 (63.3%) occurred in people known to be colonized.
Table 4 – Cases of VRE Infection by Presumed Origin of Acquisition, Québec, 2015–2016 (N, %)
Category | Origin of acquisition | Infection | |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | ||
1a | Healthcare-associated with a current hospitalization in the reporting facility | 43 | 71.7 % |
1b | Healthcare-associated with a previous hospitalization in the reporting facility | 1 | 1.7 % |
1c | Healthcare-associated with ambulatory care in the reporting facility | 3 | 5 % |
1d | Healthcare-associated with long term unit in the reporting facility | 0 | 0 % |
2 | Healthcare-associated with another facility | 2 | 3.3 % |
3 | Community-associated | 11 | 18.3 % |
4 | Unknown origin | 0 | 0 % |
| Total | 60 | 100 % |
In 2016-2017, among the 60 infections, 10 primary bloodstream infections (BSI) and 13 secondary bloodstream infections are reported (Table 5). The number of BSI observed in 2016-2017 has decreased as compared to 2015-2016 (N = 15).
Table 5 – Number of Cases of VRE Infection from All Origins by Type of Infection and Number of Complications (Secondary BSIs), Québec, 2016–2017 (N = 60)
| Infection categories | Type of infection | Infections (N) | Secondary bacteremia (N) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary bacteremia | CRBSI-MBI | 1 | - |
| CRBSI | 2 | - | |
| Non-CRBSI | 6 | - | |
| HD | 1 | - | |
| Primary infection | Urinary tract | 11 | 1 |
| Abdominal | 14 | 7 | |
| Pulmonary | 5 | 3 | |
| Surgical site | 10 | 2 | |
| Skin and soft tissues | 6 | 0 | |
| Bones and joints | 1 | 0 | |
| Others | 3 | 0 | |
| Total | 60 | 13 |
CRBSI : catheter-related bloodstream infection
MBI : mucosal barrier injury
Non-CRBSI : non- catheter-related primary bloodstream infection
HD: hemodialysis
A total of 15 deaths within 30 days of diagnosis are observed in 2016-2017, yielding a case fatality of 25.0% (Table 6). It is the first time since 2011-2012 that case fatality comes above 25%. This indicator will be monitored in future years.
Table 6 – Number of Deaths and 30-days Case Fatality Related to VRE Infections, Québec, 2011-2012 to
2015-2016
2012-2013 | 2013-2014 | 2014-2015 | 2015-2016 | 2016-2017 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VRE infections (all origins) | 112 | 101 | 105 | 96 | 60 |
| Number of deaths | 21 | 20 | 22 | 17 | 15 |
| Case fatality | 18.8 % | 19.2 % | 21.0 % | 17.7 % | 25.0 % |
Colonization Screening Protocol
In 2016-2017, the acquisition rate of HA-VRE colonization (cat. 1a and 1b) is 7.43 per 10,000 patient days for healthcare facilities participating during this last year of surveillance (Table 11) and is 7.28 per 10,000 patient days for those participating for the last five years (Table 7). Non-teaching facilities in as well as outside the Montréal health region have higher acquisition rates of HA-VRE colonization as compared to the teaching facilities (Table 7). This trend has been similar for the last five years of surveillance. A decline in VRE admission screenings in the Outaouais health region led to a drop of the acquisition rate of colonization in this region.
Table 7 – Change in the Number of Cases and Acquisition Rate of Healthcare-associated VRE Colonization (Cat. 1a and 1b) by Type of Facility and Regional Category, Québec, 2012-2013 to 2016-2017 (Acquisition rate of Healthcare-Associated VRE colonization per 10,000 patient days)
| Healthcare facilitiy categories | Vocation | 2012-2013 | 2013-2014 | 2014-2015 | 2015-2016 | 2016-2017 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Number of colonizations | Acquisition rate | Number of colonizations | Acquisition rate | Number of colonizations | Acquisition rate | Number of colonizations | Acquisition rate | Number of colonizations | Acquisition rate | ||
| Région de Montréal | Non universitaires (N = 5) | 668 | 19.24 | 772 | 22.55 | 819 | 23.8 | 909 | 25.99 | 892 | 25.66 |
| Universitaires (N = 11) | 1,778 | 17.23 | 1,910 | 18.55 | 1,776 | 17.95 | 1,982 | 20.54 | 1,566 | 16.41 | |
| Extérieur de la région de Montréal | Non universitaires (N = 55) | 700 | 3.38 | 1,072 | 5.21 | 1,652 | 7.99 | 1,139 | 5.56 | 679 | 3.34 |
| Universitaires (N = 12) | 299 | 2.48 | 488 | 4.12 | 251 | 2.16 | 263 | 2.30 | 127 | 1.11 | |
| Total (N = 83) | 3 445 | 7.40 | 4 242 | 9.23 | 4 498 | 9.85 | 4 293 | 9.53 | 3 264 | 7.28 | |
* Significant statistical difference (p ˂ 0.05) between acquisition rates of HA-VRE colonization of 2015-2016 and 2016-2017.
Note: Data are those from facilities that participated in the surveillance for a minimum of 11 periods every year between 2012-2013 and 2016-2017.
Table 8 shows the number of non-teaching facilities that specify the type of screening used at admission (55 out of 63) and during hospitalization (51 out of 63). The majority of teaching facilities specify the type of screening used at admission (23 out of 26) and during hospitalization (22 out of 26).
Table 8 – Number of Healthcare Facilities that specified the type of Screening Procedure Used at Admission and During Hospitalization by Type of Facility and Regional Category, Québec, 2016-2017
| Healthcare facilitiy categories | Vocation | Number of facilities that specified the type of screening procedure used* | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| At admission | During hospitalization | Not specified | Total | ||
| Montréal health region | Non-teaching (N = 6) | 5 | 5 | 4 | 6 |
| Teaching (N = 14) | 12 | 11 | 3 | 13** | |
| Outside the Montréal health region | Non-teaching (N = 57) | 50 | 46 | 21 | 57 |
| Teaching (N = 12) | 11 | 11 | 1 | 12 | |
| Total (N = 89) | 78 | 73 | 29 | 88 | |
* The number of facilities that reports the type of screening procedures used at admission and during hospitalization is not additive.
** One healthcare facility in the Montreal health region has not specified the type of screening.
Tables 9 and 10 feature the total number of screening tests performed at admission and during hospitalization, as well as the mean number of VRE screening tests.
Table 9 – Total Number of Screening Tests Performed at Admission and During Hospitalization by Type of Facility and Regional Category, Québec, 2016-2017
| Healthcare facilitiy categories | Vocation | Number of screening tests | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| At admission | During hospitalization | Not specified | Total | ||
| Montréal health region | Non-teaching | 22,412 | 19,681 | 2,888 | 44,981 |
| Teaching | 42,851 | 140,201 | 21,152 | 204,204 | |
| Outside the Montréal health region | Non-teaching | 131,001 | 122,781 | 75,356 | 329,138 |
| Teaching | 68,095 | 73,868 | 21,748 | 163,711 | |
| Total | 264,359 | 356,531 | 121,144 | 742,034 | |
Table 10 – Mean Number of VRE Screening Score by Type of Healthcare Facility and Regional Categories, Québec, 2016-2017 (Mean VRE Screening Tests per Admission)
| Healthcare facilitiy categories | Vocation | Mean number of VRE screening score* | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| At admission | During hospitalization | Total | ||
| Montréal health region | Non-teaching | 0.51 | 0.45 | 1.02 |
| Teaching | 0.27 | 0.89 | 1.30 | |
| Outside the Montréal health region | Non-teaching | 0.44 | 0.41 | 1.11 |
| Teaching | 0.38 | 0.41 | 0.92 | |
| Total | 0.39 | 0.53 | 1.10 | |
* The mean numbers of VRE screening score at admission and during hospitalization are not additive.
Data per facility
The HA-VRE infection rate and the percentile rankings by type of facility are shown in Figure 2 and 3. Figures 4 and 5 feature the acquisition rate and percentile ranking of HA-VRE colonization by type of facility.
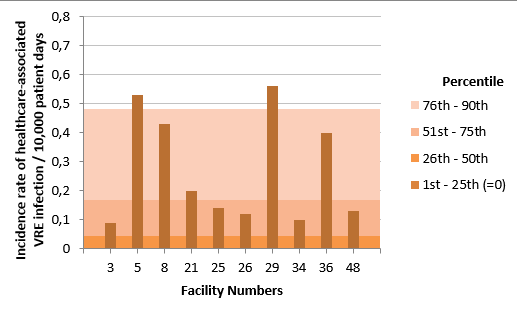
Figure 2 – Incidence Rate and Percentile Ranking of Healthcare-Associated VRE Infection (Cat. 1a and 1b) for Healthcare Facilities from the health region of Montreal, Québec, 2016-2017 (Incidence Rate per 10,000 Patient Days)
Note: Facilities 4, 6, 12, 13, 22, 38, 76, 80, 83 and 118 did not report any cases of infection in 2016-2017.
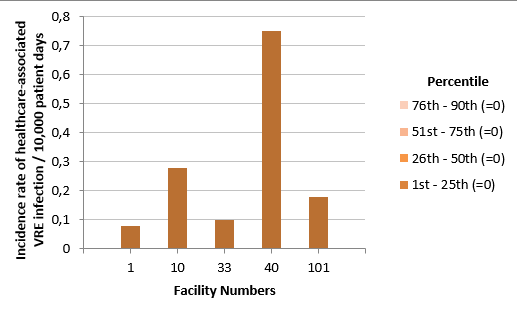
Figure 3 – Incidence Rate and Percentile Ranking of Healthcare-Associated VRE Infection (Cat. 1a and 1b) for Healthcare Facilities outside Heath Region of Montreal, Québec, 2016-2017 (Incidence Rate per 10,000 Patient Days)
Note: Facilities 2, 7, 9, 11, 14, 15, 16, 18, 19, 20, 23, 24, 27, 28, 30, 31, 32, 35, 37, 39, 41, 42, 44, 45, 46, 47, 49, 51, 52, 53, 56, 58, 59, 61, 63, 64, 65, 67, 70, 71, 72, 74, 75, 77, 81, 82, 84, 85, 86, 88, 89, 91, 95, 96, 97, 99, 100, 103, 107, 109, 111, 112, 113 and 130 did not report any cases of infection in 2016-2017.
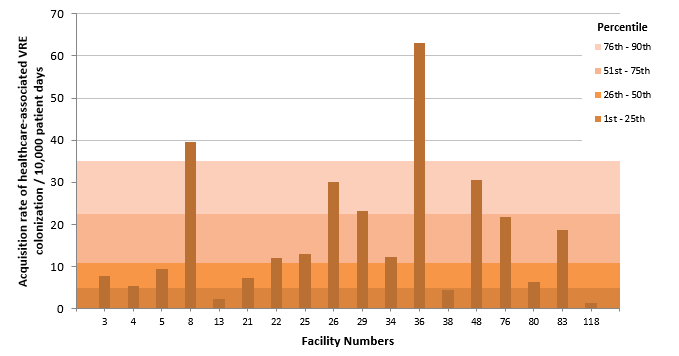
Figure 4 – Acquisition Rate of Healthcare-Associated VRE Colonization (Cat.1a and 1b) in Healthcare Facilities from the Health Region of Montreal, Québec, 2016-2017 (Acquisition Rate of Healthcare-Associated VRE Colonization per 10,000 Patient Days)
Note: Facilities 6 and 12 did not report any cases of infection in 2016-2017.
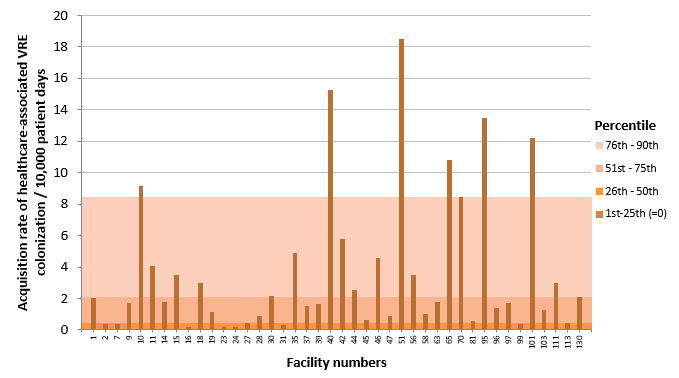
Figure 5 – Acquisition Rate of Healthcare-Associated VRE Colonization (Cat.1a and 1b) in Healthcare Facilities outside Heath Region of Montreal, Québec, 2016-2017 (Acquisition Rate of Healthcare-Associated VRE Colonization per 10,000 Patient Days)
Note: Facilities 20, 32, 33, 41, 49, 52, 53, 59, 61, 64, 67, 71, 72, 74, 75, 77, 82, 84, 85, 86, 88, 89, 91, 100, 107, 109 and 112 did not report any cases of infection in 2016‑2017.
At the local level, in 2016-2017, the HA-VRE infection rate ranges from 0 to 0.75 per 10,000 patient days, whereas the acquisition rate of HA-VRE colonization ranges from 0 to 63.10 per 10,000 patient days. A total of 28 facilities (31.5%) did not report any HA-VRE infection or colonization. A detailed summary of the surveillance data for HA-VRE infection by healthcare facility can be found in Table 11.
Table 11 – Incidence Rate of Healthcare-Associated VRE Infection (cat. 1a and 1b), Acquisition Rate of Healthcare-Associated VRE Colonization and Mean VRE Screening Tests by Admission and by Facility, Québec, 2016-2017 (Incidence Rate per 10,000 patient days [95% CI]; Acquisition Rate of Colonization per 10,000 patient days)
HR | Facility | Incidence rate of HA-VRE infection | Acquisition rate of HA-VRE colonization | Mean VRE screening tests per admission* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Number | Name | ||||
1 | 16 | HÔPITAL RÉGIONAL DE RIMOUSKI | 0 | 0.19 [0.03 ; 1.32] (1) | 1.08 |
32 | CENTRE HOSPITALIER RÉGIONAL DU GRAND-PORTAGE | 0 | 0 | 1.04 | |
61 | HÔPITAL NOTRE-DAME-DE-FATIMA | 0 | 0 | 0.24 | |
71 | HÔPITAL DE MATANE | 0 | 0 | 0.94 | |
77 | HÔPITAL D'AMQUI | 0 | 0 | 2.01 | |
84 | HÔPITAL DE NOTRE-DAME-DU-LAC | 0 | 0 | 1.08 | |
| BAS-SAINT-LAURENT | 0 | 0.09 [0.01 ; 0.61] (1) | 1.06 | |
2 | 20 | HÔPITAL DE CHICOUTIMI | 0 | 0 | 0.65 |
67 | HÔPITAL ET CENTRE DE RÉADAPTATION DE JONQUIÈRE | 0 | 0 | 0.73 | |
74 | HÔPITAL DE DOLBEAU-MISTASSINI | 0 | 0 | 1.1 | |
88 | HÔPITAL. CLSC ET CENTRE D'HÉBERGEMENT DE ROBERVAL | 0 | 0 | 0.88 | |
100 | HÔPITAL DE LA BAIE | 0 | 0 | 0.79 | |
112 | HÔPITAL D'ALMA | 0 | 0 | 0.63 | |
| SAGUENAY–LAC-SAINT-JEAN | 0 | 0 | 0.72 | |
3 | 2 | HÔPITAL DE L'ENFANT-JÉSUS | 0 | 0.38 [0.16 ; 0.92] (5) | 1.08 |
7 | PAVILLON L'HÔTEL-DIEU DE QUÉBEC | 0 | 0.35 [0.11 ; 1.10] (3) | 1.22 | |
24 | HÔPITAL DU SAINT-SACREMENT | 0 | 0.19 [0.03 ; 1.37] (1) | 1.02 | |
27 | PAVILLON CENTRE HOSPITALIER DE L'UNIVERSITÉ LAVAL | 0 | 0.43 [0.18 ; 1.03] (5) | 0.99 | |
28 | PAVILLON SAINT-FRANCOIS D'ASSISE | 0 | 0.90 [0.45 ; 1.79] (8) | 1.14 | |
33 | INSTITUT UNIVERSITAIRE DE CARDIOLOGIE ET DE PNEUMOLOGIE DE QUÉBEC | 0.10 [0.01 ; 0.72] (1) | 0 | 1.24 | |
59 | HÔPITAL DE BAIE-SAINT-PAUL | 0 | 0 | 1.37 | |
86 | HÔPITAL DE LA MALBAIE | 0 | 0 | 1.1 | |
| CAPITALE-NATIONALE | 0.02 [0.00 ; 0.10] (1) | 0.37 [0.24 ; 0.56] (22) | 1.12 | |
4 | 23 | HÔTEL-DIEU D'ARTHABASKA | 0 | 0.21 [0.03 ; 1.46] (1) | 1.14 |
31 | PAVILLON SAINTE-MARIE | 0 | 0.32 [0.12 ; 0.84] (4) | 0.72 | |
41 | HÔPITAL DU CENTRE-DE-LA-MAURICIE | 0 | 0 | 0.88 | |
44 | HÔPITAL SAINTE-CROIX | 0 | 2.53 [1.52 ; 4.20] (15) | 1.27 | |
85 | CENTRE DE SANTÉ ET DE SERVICES SOCIAUX DU HAUT-SAINT-MAURICE | 0 | 0 | 0.67 | |
| MAURICIE ET CENTRE-DU-QUÉBEC | 0 | 0.69 [0.45 ; 1.07] (20) | 0.89 | |
5 | 15 | HÔPITAL FLEURIMONT | 0 | 3.50 [2.54 ; 4.83] (37) | 0.54 |
30 | HOTEL-DIEU DE SHERBROOKE | 0 | 2.18 [1.32 ; 3.61] (15) | 0.58 | |
46 | HÔPITAL DE GRANBY | 0 | 4.57 [2.98 ; 7.01] (21) | 1.22 | |
49 | CENTRE DE SANTÉ ET DE SERVICES SOCIAUX MEMPHRÉMAGOG | 0 | 0 | 0.97 | |
75 | CENTRE DE SANTÉ ET DE SERVICES SOCIAUX DU GRANIT | 0 | 0 | 0.06 | |
99 | HÔPITAL BROME-MISSISQUOI-PERKINS | 0 | 0.37 [0.05 ; 2.59] (1) | 0.7 | |
| ESTRIE | 0 | 2.74 [2.18 ; 3.44] (74) | 0.66 | |
6 | 3 | GLEN - ROYAL VICTORIA | 0.09 [0.01 ; 0.68] (1) | 7.69 [6.20 ; 9.53] (83) | 0.99 |
4 | HÔPITAL NOTRE-DAME DU CHUM | 0 | 5.47 [4.22 ; 7.09] (57) | 1.87 | |
5 | HÔPITAL GÉNÉRAL JUIF | 0.53 [0.27 ; 1.02] (9) | 9.43 [8.07 ; 11.02] (159) | 0.91 | |
6 | GLEN - ENFANTS | 0 | 0 | 0.08 | |
8 | PAVILLON MAISONNEUVE/PAVILLON MARCEL-LAMOUREUX | 0.43 [0.22 ; 0.86] (8) | 39.57 [36.82 ; 42.53] (738) | 1.1 | |
12 | CENTRE HOSPITALIER UNIVERSITAIRE SAINTE-JUSTINE | 0 | 0 | 0.13 | |
13 | INSTITUT DE CARDIOLOGIE DE MONTRÉAL | 0 | 2.25 [1.21 ; 4.18] (10) | 2.26 | |
21 | HÔPITAL SAINT-LUC DU CHUM | 0.20 [0.05 ; 0.78] (2) | 7.38 [5.89 ; 9.25] (75) | 1.59 | |
22 | HÔTEL-DIEU DU CHUM | 0 | 12.08 [9.72 ; 15.02] (81) | 2.63 | |
25 | HÔPITAL DU SACRÉ-COEUR DE MONTRÉAL | 0.14 [0.04 ; 0.54] (2) | 13.03 [11.31 ; 15.01] (191) | 1.93 | |
26 | HÔPITAL DE VERDUN | 0.12 [0.02 ; 0.87] (1) | 30.03 [26.51 ; 34.02] (247) | 0.83 | |
29 | HÔPITAL GÉNÉRAL DE MONTRÉAL | 0.56 [0.21 ; 1.49] (4) | 23.07 [19.80 ; 26.87] (165) | 1.58 | |
34 | HÔPITAL SANTA CABRINI | 0.10 [0.01 ; 0.68] (1) | 12.16 [10.20 ; 14.50] (124) | 1.18 | |
36 | HÔPITAL GÉNÉRAL DU LAKESHORE | 0.40 [0.13 ; 1.24] (3) | 63.10 [57.67 ; 69.04] (475) | 1.48 | |
38 | HÔPITAL JEAN-TALON | 0 | 4.30 [2.80 ; 6.60] (21) | 1.24 | |
48 | CENTRE HOSPITALIER DE ST. MARY | 0.13 [0.02 ; 0.95] (1) | 30.54 [26.85 ; 34.74] (231) | 1.52 | |
76 | HOPITAL DE LACHINE | 0 | 21.80 [15.93 ; 29.84] (39) | 0 | |
80 | HÔPITAL FLEURY | 0 | 6.28 [4.24 ; 9.30] (25) | 1.5 | |
83 | HÔPITAL DE LASALLE | 0 | 18.66 [14.39 ; 24.19] (57) | 0.12 | |
118 | HÔPITAL NEUROLOGIQUE DE MONTRÉAL | 0 | 1.30 [0.42 ; 4.04] (3) | 1.19 | |
| MONTRÉAL | 0.20 [0.14 ; 0.28] (32) | 17.13 [16.51 ; 17.78] (2781) | 1.24 | |
7 | 39 | HÔPITAL DE GATINEAU | 0 | 1.64 [0.88 ; 3.05] (10) | 0.01 |
40 | HÔPITAL DE HULL | 0.75 [0.31 ; 1.80] (5) | 15.28 [12.58 ; 18.55] (102) | 0.14 | |
51 | HÔPITAL DE MANIWAKI | 0 | 18.47 [12.58 ; 27.13] (26) | 1.31 | |
95 | HÔPITAL DU PONTIAC | 0 | 13.48 [8.26 ; 22.00] (16) | 1.84 | |
111 | HÔPITAL DE PAPINEAU | 0 | 2.99 [1.34 ; 6.65] (6) | 0.12 | |
| OUTAOUAIS | 0.29 [0.12 ; 0.69] (5) | 9.21 [7.89 ; 10.75] (160) | 0.28 | |
8 | 47 | HÔPITAL DE ROUYN-NORANDA | 0 | 0.86 [0.22 ; 3.41] (2) | 0.45 |
52 | HÔPITAL D'AMOS | 0 | 0 | 0.22 | |
65 | HÔPITAL ET CLSC DE VAL-D'OR | 0 | 10.79 [7.29 ; 15.97] (25) | 0.87 | |
70 | CENTRE DE SOINS DE COURTE DURÉE LA SARRE | 0 | 8.46 [4.03 ; 17.75] (7) | 1.1 | |
82 | PAVILLON SAINTE-FAMILLE | 0 | 0 | 0.81 | |
| ABITIBI-TÉMISCAMINGUE | 0 | 4.17 [2.98 ; 5.83] (34) | 0.57 | |
9 | 64 | HÔPITAL LE ROYER | 0 | 0 | 0.42 |
72 | HÔPITAL ET CENTRE D'HÉBERGEMENT DE SEPT-ÎLES | 0 | 0 | 0.08 | |
| CÔTE-NORD | 0 | 0 | 0.24 | |
10 | 96 | CENTRE DE SANTÉ DE CHIBOUGAMAU | 0 | 1.37 [0.19 ; 9.71] (1) | 0.56 |
| NORD-DU-QUÉBEC | 0 | 1.37 [0.19 ; 9.71] (1) | 0.56 | |
11 | 53 | HÔPITAL DE CHANDLER | 0 | 0 | 0.82 |
91 | HÔPITAL HÔTEL-DIEU DE GASPÉ | 0 | 0 | 0.19 | |
97 | HÔPITAL DE MARIA | 0 | 1.70 [0.55 ; 5.26] (3) | 1.71 | |
107 | HÔPITAL DE L'ARCHIPEL | 0 | 0 | 0.34 | |
109 | HÔPITAL DE SAINTE-ANNE-DES-MONTS | 0 | 0 | 0.26 | |
| GASPÉSIE–ÎLES-DE-LA-MADELEINE | 0 | 0.54 [0.17 ; 1.68] (3) | 0.83 | |
12 | 18 | HÔTEL-DIEU DE LÉVIS | 0 | 2.99 [1.99 ; 4.50] (23) | 1.01 |
63 | HÔPITAL DE SAINT-GEORGES | 0 | 1.77 [0.84 ; 3.71] (7) | 0.94 | |
89 | HÔPITAL DE MONTMAGNY | 0 | 0 | 1.12 | |
113 | HÔPITAL DE THETFORD MINES | 0 | 0.45 [0.06 ; 3.16] (1) | 0.79 | |
| CHAUDIÈRE-APPALACHES | 0 | 1.99 [1.40 ; 2.83] (31) | 0.97 | |
13 | 19 | HÔPITAL CITÉ DE LA SANTÉ | 0 | 1.15 [0.74 ; 1.78] (20) | 0.85 |
| LAVAL | 0 | 1.15 [0.74 ; 1.78] (20) | 0.85 | |
14 | 11 | HÔPITAL PIERRE-LE GARDEUR | 0 | 4.08 [3.06 ; 5.45] (46) | 0.92 |
14 | CENTRE HOSPITALIER RÉGIONAL DE LANAUDIÈRE | 0 | 1.77 [1.11 ; 2.81] (18) | 1.61 | |
| LANAUDIÈRE | 0 | 2.99 [2.34 ; 3.82] (64) | 1.24 | |
15 | 45 | HÔPITAL DE SAINT-EUSTACHE | 0 | 0.66 [0.30 ; 1.47] (6) | 0.99 |
56 | CENTRE DE SANTÉ ET DE SERVICES SOCIAUX D'ARGENTEUIL | 0 | 3.52 [1.46 ; 8.46] (5) | 3.05 | |
81 | HÔPITAL DE MONT-LAURIER | 0 | 0.56 [0.08 ; 4.03] (1) | 2.08 | |
101 | HÔPITAL RÉGIONAL DE SAINT-JÉRÔME | 0.18 [0.04 ; 0.75] (2) | 12.21 [10.30 ; 14.48] (132) | 2.19 | |
103 | HÔPITAL LAURENTIEN | 0 | 1.28 [0.48 ; 3.41] (4) | 2.19 | |
| LAURENTIDES | 0.08 [0.02 ; 0.30] (2) | 5.65 [4.81 ; 6.64] (148) | 1.77 | |
16 | 1 | HÔPITAL CHARLES LEMOYNE | 0.08 [0.01 ; 0.55] (1) | 2.04 [1.39 ; 3.00] (26) | 1.12 |
9 | HÔPITAL DU HAUT-RICHELIEU | 0 | 1.72 [1.04 ; 2.85] (15) | 1.45 | |
10 | HÔPITAL PIERRE-BOUCHER | 0.28 [0.09 ; 0.88] (3) | 9.15 [7.50 ; 11.16] (97) | 0.99 | |
35 | HÔPITAL HONORÉ-MERCIER | 0 | 4.90 [3.46 ; 6.93] (32) | 1.5 | |
37 | HÔTEL-DIEU DE SOREL | 0 | 1.49 [0.71 ; 3.12] (7) | 1.83 | |
42 | CENTRE HOSPITALIER ANNA-LABERGE | 0 | 5.81 [4.31 ; 7.84] (43) | 2.12 | |
58 | HÔPITAL DU SUROÎT | 0 | 0.99 [0.44 ; 2.21] (6) | 1.34 | |
130 | HÔPITAL BARRIE MEMORIAL | 0 | 2.07 [0.52 ; 8.28] (2) | 2 | |
| MONTÉRÉGIE | 0.07 [0.03 ; 0.18] (4) | 3.95 [3.47 ; 4.50] (228) | 1.38 | |
|
| Total | 0.09 [0.07 ; 0.12] (44) | 7.43 [7.19 ; 7.68] (3587) | 1.1 |
* Number of screening tests divided by number of admissions.
HR: Health region
Author
Comité de surveillance provinciale des infections nosocomiales (SPIN)
Editorial Committee
Christophe Garenc, Direction des risques biologiques et de la santé au travail. Institut national de santé publique du Québec
Danielle Moisan, Centre hospitalier régional du Grand-Portage
Muleka Ngenda-Muadi, Direction des risques biologiques et de la santé au travail. Institut national de santé publique du Québec
Claude Tremblay, Centre hospitalier universitaire de Québec – Université Laval
Mélissa Trudeau, Direction des risques biologiques et de la santé au travail. Institut national de santé publique du Québec
Isabelle Rocher, Direction des risques biologiques et de la santé au travail. Institut national de santé publique du Québec
Patrice Vigeant, CISSS de la Montérégie-Ouest - Hôpital du Suroît
Jasmin Villeneuve, Direction des risques biologiques et de la santé au travail. Institut national de santé publique du Québec


![Figure 1 – Incidence Rate of Healthcare-Associated VRE Infection (Cat. 1a and 1b) by Type of Facility and Regional Category (N = 83), Québec, 2012–2013 to 2016–2017 (Incidence Rate per 10,000 Patient Days [95% CI]) Figure 1 – Incidence Rate of Healthcare-Associated VRE Infection (Cat. 1a and 1b) by Type of Facility and Regional Category (N = 83), Québec, 2012–2013 to 2016–2017 (Incidence Rate per 10,000 Patient Days [95% CI])](/sites/default/files/images/maladies-infectieuses/spin/erv/2017/en/figure1.png)